<< Hide Menu
2.1 Cell Structure: Subcellular Components
5 min read•november 18, 2024
Haseung Jun
Tejas Bhartiya
Haseung Jun
Tejas Bhartiya
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Describe structures and functions of organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
- Explain how different organelles contribute to cell health and function.
- Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structures.
- Analyze the impact of organelle dysfunction on cell processes.
- Relate organelle organization to cellular activities like energy production and protein synthesis.
Subcomponents
A cell has subcomponents, or organelles that perform different jobs! Even a tiny cell has a lot going on, so it needs different organelles to do different jobs. Let's take a look at these components 🧐
Plasma Membrane
Arguably the most important component! The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. This means that the membrane is made up of two lipid layers. Phospholipids also have two special properties. The head is hydrophilic, which means it likes water. The tail, on the other hand, is hydrophobic, meaning it doesn't like water. The membrane is then set up in a way so that the head is pointing towards the inside and outside of the cell (thus touching water) while the tail is nested between the sandwich of the heads.
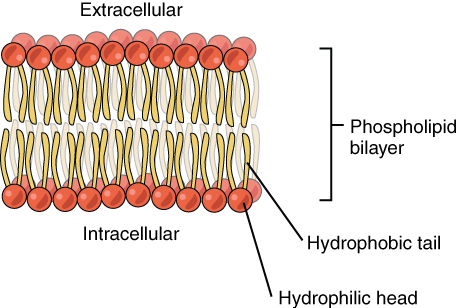
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
The membrane is also known as the fluid-mosaic model, which means that the membrane is very flexible. It's also made up of different proteins along the membrane, and these proteins, which you'll learn in future units, act as transporters for things that can't go through the hydrophobic tail section.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the largest component of the cell. It's the "brain" of the cell and directs everything the cell does. It's also in charge of reproduction because it contains all the genetic information (DNA). The nucleolus is where the ribosomes are assembled within the DNA.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are made of primarily ribosomal RNA (rRNA). They are the site of translation and are responsible for making all of the proteins for the cell. There are 2 kinds found in different locations.
Free ribosomes are in the cytosol and make proteins that stay in the cell for various functions. Bound ribosomes are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and mainly make proteins for export. Ribosomes synthesize proteins according to mRNA sequences that they receive during the process of translation.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), made up of two parts, serves to make other products that the cell needs. The smooth ER has many functions. It performs synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, detoxification of drugs and poisons, and stores calcium ions.
The rough ER, is called rough because it has ribosomes attached to its surface, making it "rough". It secretes proteins made by bound ribosomes. Proteins then are moved to the transitional ER, where they are wrapped in a transport vesicle to head to the Golgi apparatus.

Image courtesy of WikiMedia Commons.
The Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus, shown above, modifies, stores, and sends proteins that come from the rough ER. Things like glycoproteins are modified in the Golgi. There are 2 sides on the Golgi apparatus, cis and trans face. Vesicles enter the Golgi apparatus via the cis face and depart via the trans face. It is in the Golgi that proteins are packaged and distributed to desired locations. These proteins are packaged in little sacs called vesicles, which is pinched off from the Golgi. The Golgi is also involved in the production of lysosomes.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria have a double membrane, which is a phospholipid bilayer. The outer membrane is smooth, while the inner has many folds, called cristae. These folds help to increase the surface area available for the Electron Transport Chain. The inside of the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix, which is the site of the Krebs Cycle. The Mitochondria creates ATP for the cell to use via cellular respiration. Because the mitochondria also have their own circular DNA, most biologists think the mitochondria was its own organism until it was swallowed by eukaryotes (us!). The structure of the mitochondria is important to know because it comes in handy with cellular respiration. The mitochondrial contains an outer membrane and inner membrane, making up its double membrane. The inner membrane consists of folds called cristae, which is where most of the ATP production happens. The fold increases surface area and thus efficiency. Inside the inner membrane is the matrix.
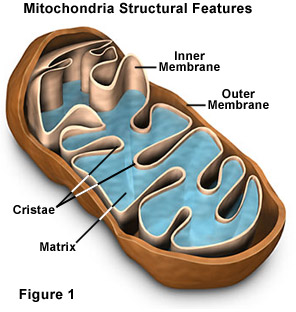
Image Courtesy of Molecular Expressions
Lysosomes
Lysosomes hydrolyze most foods, amino acids, and other molecules. The inside of lysosome is extremely acidic. Lysosomes can digest foods by using phagocytosis or engulfing nutrients to digest them. The hydrolytic enzymes inside of the lysosome work to break down anything that comes into contact with it. The lysosome is also used to recycle and digest old or damaged parts of the cell. Think of it as the trash can of the cell! It's also in charge of apoptosis, which is programmed cell death. Essentially, the lysosome bursts, causing the acid to kill the cell.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are large vesicles which store many different things, such as food or water. Many unicellular eukaryotes have contractile vacuoles to pump water out of the cell. Also, plants generally have a large central water vacuole which stores water and ions.
Chloroplast
The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis. These organelles have a double membrane and have green pigments called chlorophyll that allow for the absorption of photons. The chloroplast is made up of the stroma, or liquid filling of the chloroplast, and the thylakoids, flat sacs of membranes that allow for the absorption of light. The chloroplast is in charge of photosynthesis.
Centrioles
Centrioles are small, cylindrical components of the cell and are mostly active during cell division. You'll learn more about the role of centrioles in the mitosis unit, but basically, it pulls apart chromosomes by producing microtubules.
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant cells have something called cell walls, which is made out of cellulose. It's mostly a protective outer layer other than the membrane. Animal cells don't have this. In contrast, animal cells have centrioles, while plant cells do not.
When thinking about the differences of plant cells and animal cells, also try to think about prokaryotic cells. On the AP exam, there will be questions that can only be answered if you can correctly identify if the cell is an animal, plant, or prokaryotic cell. That's why key identifiers are important to memorize.
| Prokaryote 🧫 | Plant Cell 🌼 | Animal Cell 🐄 | |
| Cell wall | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Plasma membrane | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Nucleus | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Centrioles | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ribosomes | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Also keep in mind, a prokaryotic cell does not have any subcomponents like a lysosome or golgi body. Instead it only has a flagella, which acts like a tail to help movement. Other than that, a prokaryotic cell is pretty much an empty capsule with DNA and ribosomes.
Now quiz time! Try to identify which cell is eukaryotic and which is prokaryotic! Remember to think about key components that give you an immediate hint, and look for those when looking at cell pictures!
Quick Quiz: Can you identify which Cell is Eukaryotic and which is Prokaryotic?
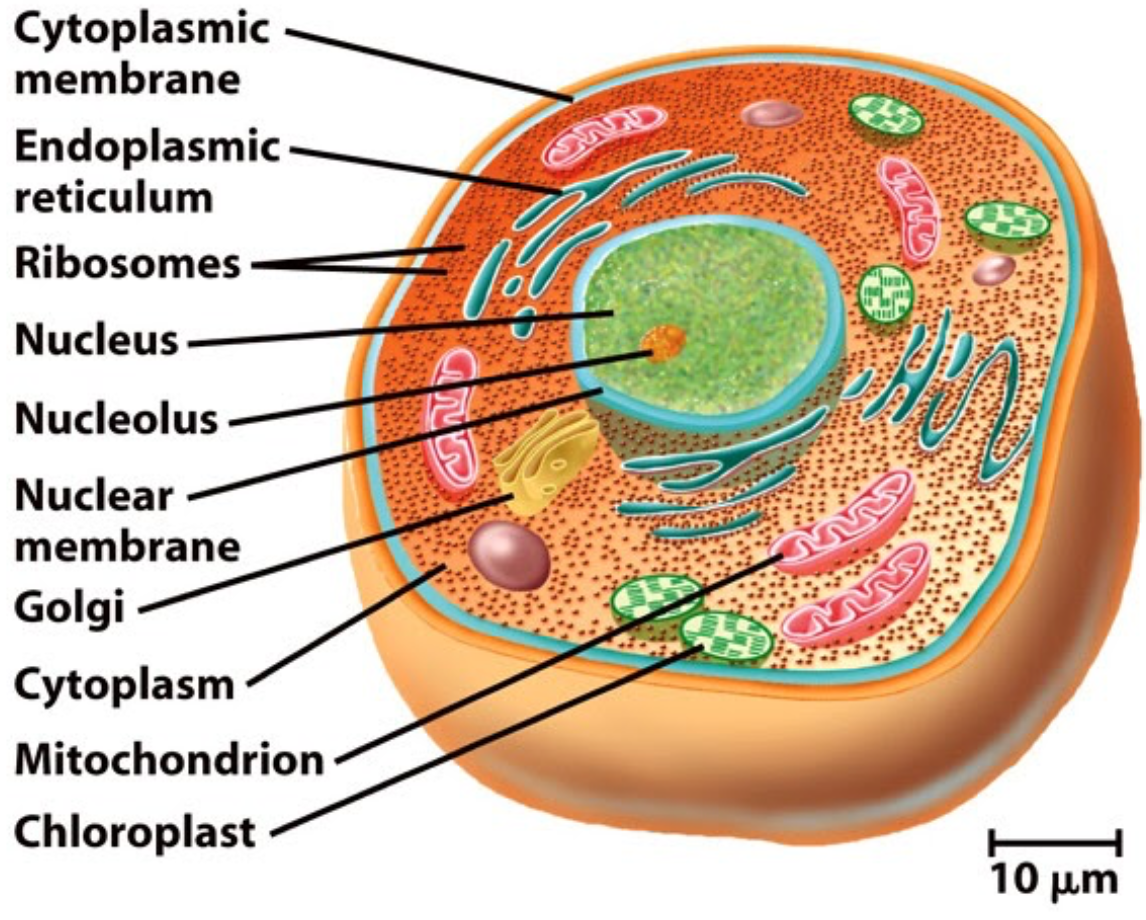
Image courtesy of Flickr.
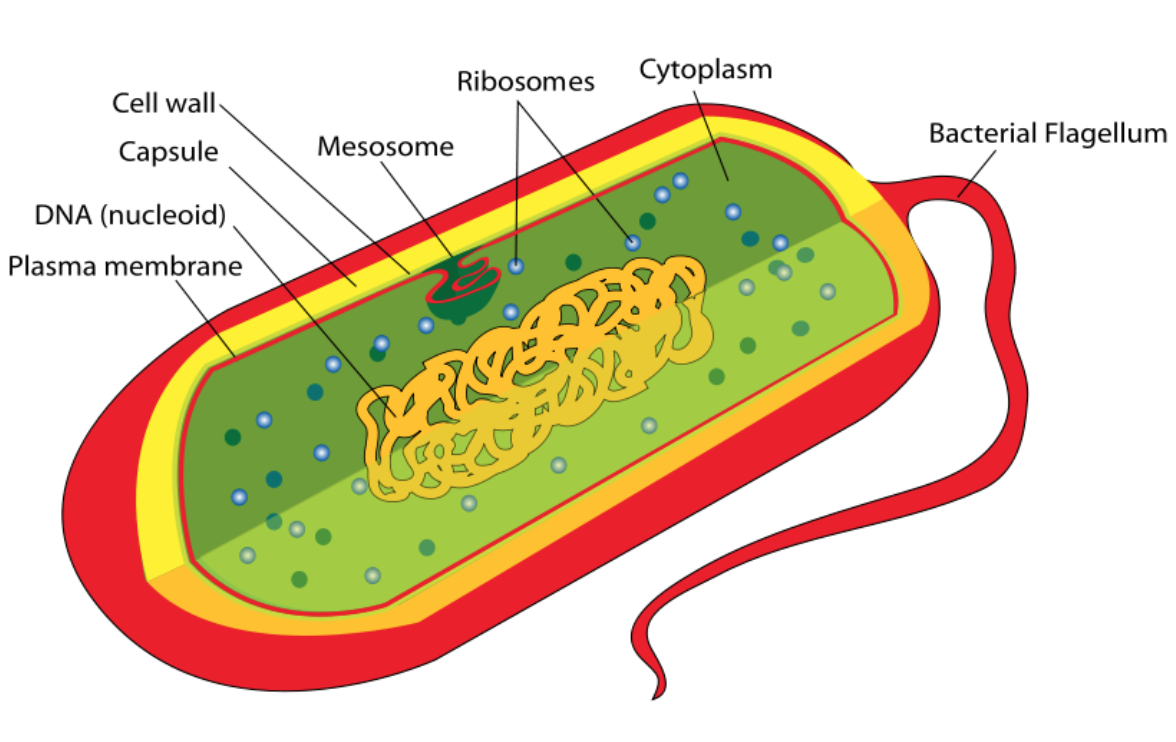
Image courtesy of Wikipedia.org.
💥
💥
💥
💥
💥
💥
Answer: First picture is eukaryotic, second picture is prokaryotic.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.