<< Hide Menu
Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Explain natural selection and the role of environmental pressures.
- Describe conditions needed for natural selection to occur.
- Relate natural selection to adaptation and population trait changes.
- Predict evolutionary outcomes based on selective pressures.
- Analyze natural selection’s impact on population diversity.
Getting to Know Evolution and Survival of the Fittest
As you've glimpsed in the unit overview (via the previous section), this unit doubles down on the concept of evolution. Evolution refers to the process by which populations of living organisms change over time, characterized by a change in the genetic makeup. This change is driven by natural selection, which is the process by which certain variations in traits become more or less common in a population depending on how well those variations help the organisms that possess them to survive and reproduce. 🎰
Ever Heard of "Survival of the Fittest"?
Natural selection is one of the main components of evolution. It can actually change the phenotypic ratios of species and/or populations using “survival of the fittest.” To summarize this idea in a sentence: those that have traits that are more advantageous to their survival are more likely to survive and pass those traits onto their offspring.
Theory of Evolution
This thought was first introduced by Charles Darwin in his Theory of Evolution. After studying birds in South America, he proposed this theory based on three major propositions: 🐦
- Species change over time
- Divergent species share a common ancestor
- Natural selection is the mechanism that produces these changes in species/populations In a population of organisms, there is often variation in traits among individuals. Some of these variations may be beneficial and help the organism to survive and reproduce better than others. According to Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection, these beneficial variations are more likely to be passed on to subsequent generations. This process can lead to changes in the genetic makeup of a population over time, and it can result in the evolution of new species.
Darwin's theory of natural selection was based on several key observations. One of these observations is that there is more variation among individuals in a population than can be sustained by the resources available in their environment. This leads to a struggle for survival among individuals, and it means that not all individuals will be able to survive and reproduce.
Another important observation that Darwin made is that different traits tend to be inherited in different ways. Some traits are determined by a single gene, while others are determined by many genes. This means that some traits are more likely to be passed on to subsequent generations than others, and it also means that different traits are more likely to be affected by selection.
Natural selection acts by differentially determining the survival and reproduction of individual organisms with different genetic variation. Individuals with favorable variations in certain traits will have a greater chance of survival and will tend to pass on these beneficial traits to their offspring. Over many generations, this process can result in a change in the frequency of these favorable variations in the population, this is often referred to as adaptation. 💯
Thus, natural selection is the driving force behind the process of evolution, leading to the development of new species and the extinction of others, based on the adaptation of certain traits to specific environments!
Darwin's Finches
Darwin witnessed natural selection firsthand when he realized that the finch (bird) species had adapted to food that they could access. Some had bigger beaks for cracking bigger nuts, while others had smaller beaks to reach the smaller nuts in smaller places. These species may have actually originated with the same species, but diverged with two different identifying traits that ultimately played an integral role in their survival. 🌱
Here's the complete story:
Darwin's finches, also known as Galapagos finches, are a group of small birds that are found on the Galapagos Islands, a chain of islands off the coast of Ecuador. These birds were studied by Charles Darwin during the voyage of the HMS Beagle in the 1830s, and they played a key role in shaping his ideas about evolution and natural selection. 🇪🇨
When Darwin visited the Galapagos Islands, he observed that each island had its own unique finch species, and that these species were different in terms of their beak size and shape. He also noticed that the finches on different islands had beaks that were adapted to their specific food sources. For example, finches on some islands had strong, heavy beaks that were well-suited for cracking open hard seeds, while finches on other islands had thinner, more pointed beaks that were better suited for probing for insects.
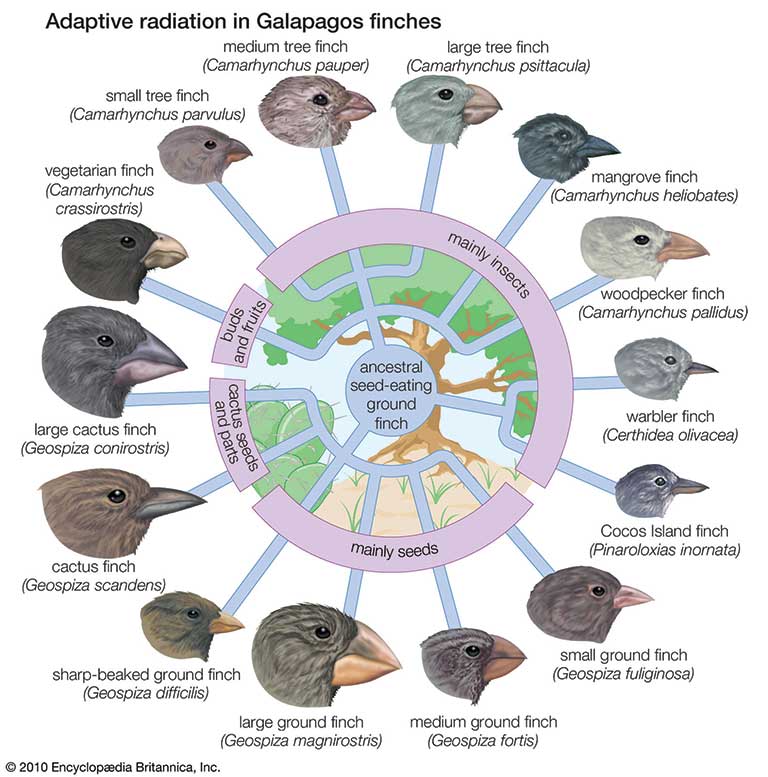
Source: Britannica
Darwin realized that these differences in beak shape and size were not arbitrary, but were instead the result of a process of adaptation to the different environments found on each island. He proposed that a common ancestor of all the finches had colonized the Galapagos Islands and then gradually diverged into different species as they adapted to the different conditions on each island.
He also noticed that the beak variations that were the most beneficial for survival and reproduction had a higher likelihood of being passed to the offspring, and thus, these variations had been selected through time in order to adapt to the different conditions. He called this process natural selection.
This was one of the main observations that helped Darwin to formulate his theory of evolution by natural selection. He later used these finches as an example to explain how natural selection could lead to the development of new species over time and how the structures of living organisms become adapted to their environment.
The study of Darwin's finches continues to this day and they have become an important model organism for studying the process of adaptation and speciation. Research on Darwin's finches is helping to illuminate the genetic mechanisms underlying adaptation and how natural selection acts on the genome! 🧬

Source: Giphy.
Fitness
Evolutionary fitness refers to the phenotypes that are directly related to the survival of a species or population. If a trait is known for its “fitness”, it just means that it aids in the survival of that particular species or population. Some examples of this would be coloring that can aid with camouflage. 🌎 The individuals without an advantageous phenotype would be spotted by predators much faster than those that blend in with their surroundings, and would therefore die before they can reproduce and pass their disadvantageous traits onto offspring. Therefore, that phenotype could eventually die out altogether, leaving only those with evolutionary fitness left to survive and reproduce.
In fact, the surrounding environment plays into natural selection as well. In any biome, the population will be affected by both biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors.
Examples of biotic factors would be
-
vegetation
-
predators
-
prey, etc Abiotic factors would include things like
-
soil
-
temperature
-
other non-living environmental components.
More About Environments
The environment in which a population of organisms lives can have a significant impact on the rate and direction of evolution. The stability or fluctuation of the environment can affect the selective pressures on the population and thus the genetic variations that are more likely to be passed on to subsequent generations. 📈
A biotic environment refers to the living components of an ecosystem, such as other organisms and their interactions. An abiotic environment refers to the non-living components of an ecosystem, such as climate, geology, and physical features.
A stable biotic environment will have a lower rate of evolution since the selective pressures on the population are constant, but if there are fluctuating conditions within the biotic environment such as changes in competitors, predators or prey, this will increase the pressure of natural selection on the population.
Similarly, a stable abiotic environment will have a lower rate of evolution, but fluctuating abiotic conditions such as changes in temperature, precipitation, or resource availability, can increase the selective pressure on the population and drive faster rates of evolution.
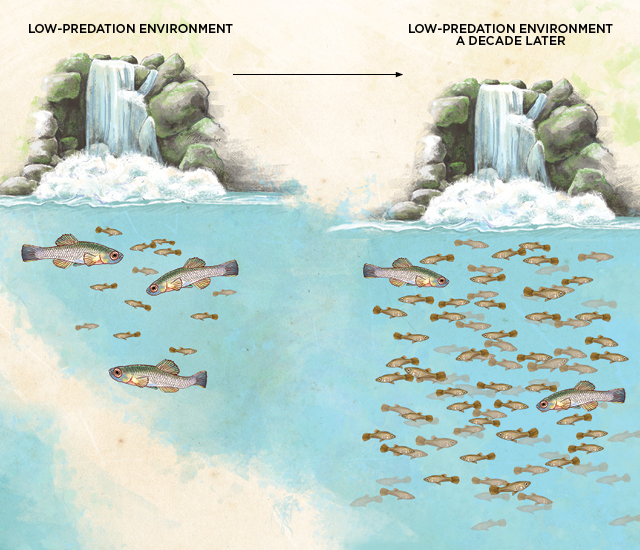
Source: The Scientist
The direction of evolution can also be affected by environmental changes. For example, a population living in a changing environment may evolve in a direction that allows it to better cope with the new conditions. Such as the famous example of the Darwin's finches, where different beak variations were selected to adapt to different food sources, depending on the island they lived on.
Therefore, by understanding how the environment affects the rate and direction of evolution, scientists can gain insights into how populations adapt to changing conditions over time! 🕝
Check out the AP Bio Unit 7 Replays or watch the 2021 Unit 7 Cram

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.