<< Hide Menu
3.9 Challenges of Political and Social Cleavages
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Isabela Padilha
Kelly Cotton
Isabela Padilha
Kelly Cotton
Unit 3 - Challenges of Political and Social Cleavages 🧩
You read in the previous guide about the importance of studying social cleavages and saw how they play a role in each of our core countries. In this guide you will learn more about the difficulties that they pose to their governments. You must keep in mind that social cleavages play a role in a government, no matter what type of regime it is. Even the most stable democracies have seen the emergence of radical/terrorists religious elements that sprung from long-term cleavages. Democracies and Autocracies all have cleavages, but the difference is how these governments deal with them.
3.9: Challenges of Political and Social Cleavages
How do cleavages affect governments?
- Conflicting interests and competition among groups and political parties 🆚 In the previous guide we discussed the concept of coinciding cleavages, which can lead to complex and multifaceted conflicts in society. Many times, these groups form parties that are picking against another specific party. This can can cause polarization in the political system, but it may also be resolved through dialogue and negotiation. 🗣
Example: The Zapatista Movement grew its activity after the signing of the NAFTA - the free trade agreement between the US, Mexico and Canada - because they believed that it would harm indigenous communities. However, there were also other groups that believed that it was an excellent advancement for Mexico to be more integrated in the world market.
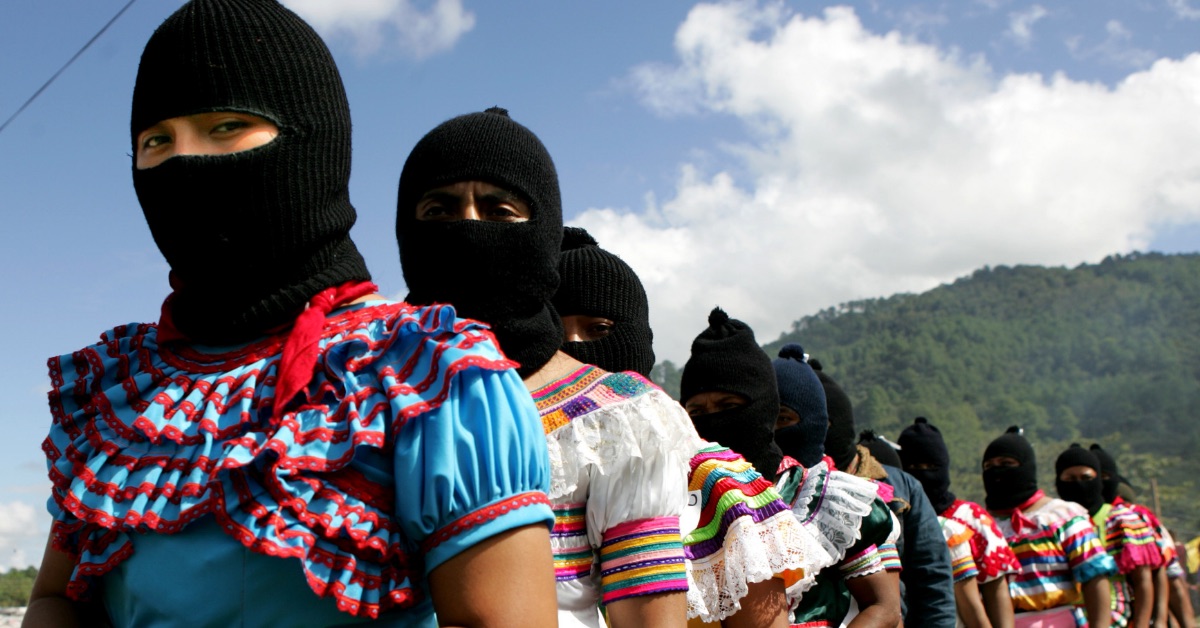

- Perceived lack of governmental authority and legitimacy 🤨 The emergence of cleavages may also affect the perception of the government, which causes these groups to want more autonomy from the state or a complete separation from it. The lack of control of the government over these groups may also cause a perception of lack of authority.
Example: In the UK, there has been a growing sentiment among the Scottish people for full separation from the mainland. The countries share a complex history, having shared a monarchy since the 14th Century. But, Scotland has its own legal system, government and cultural identity. The process of the BREXIT has increased these tensions, and the Scottish National Party continues to advocate for a second independence referendum.
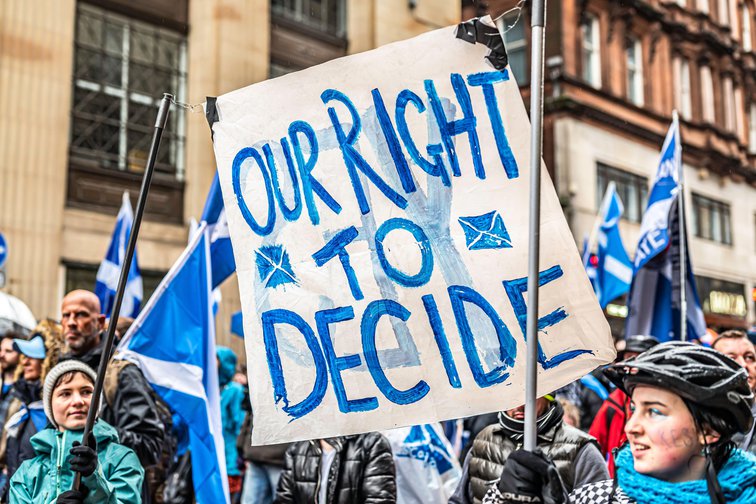

- Pressure for autonomy/secession, intergroup conflict, terrorism, and civil war ⚠️ In many cases, some long-term cleavages gather hard power and may become a threat to other cleavages, the government, and even the population as a whole.
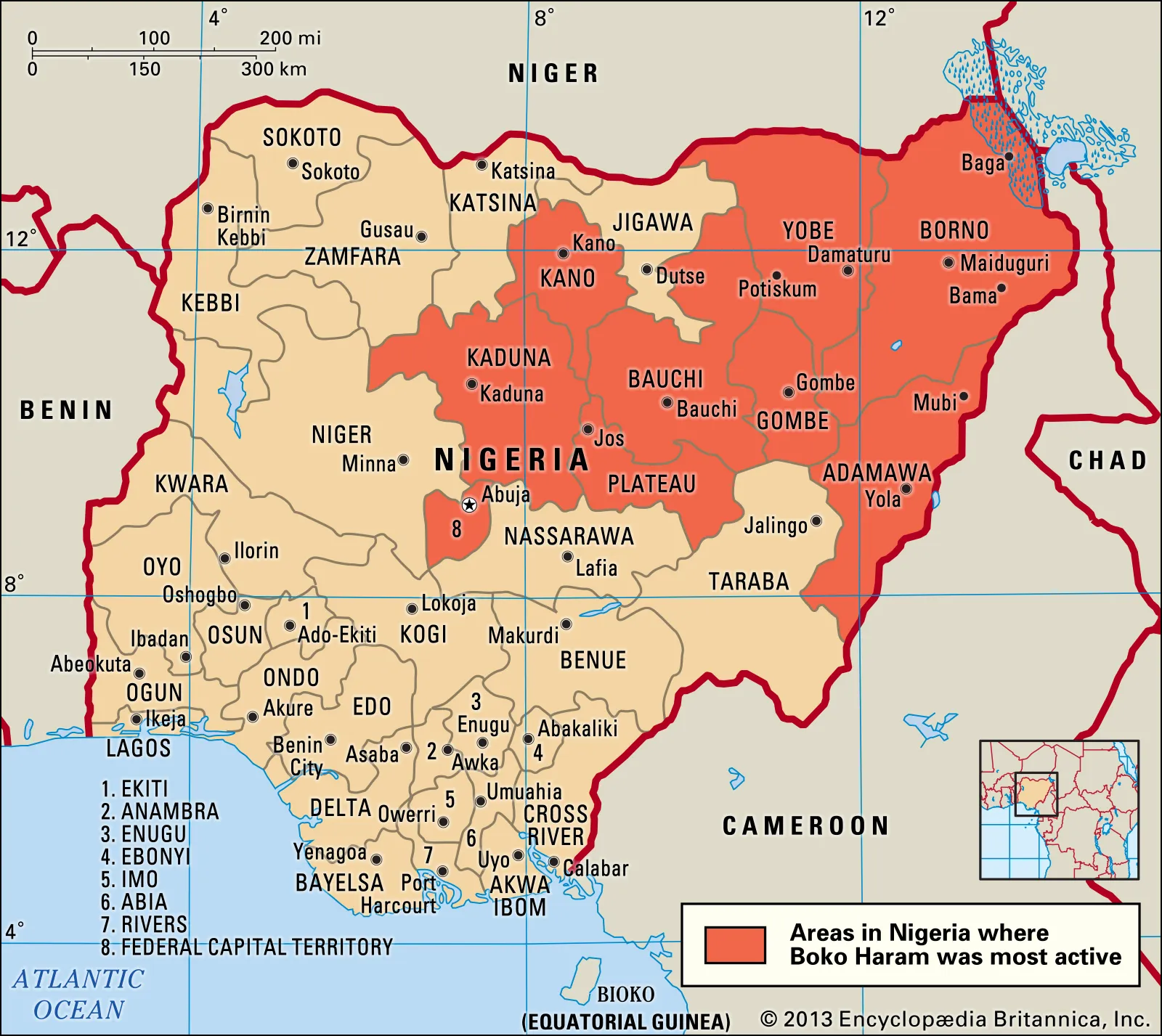
Example: Boko Haram in Nigeria has grown so much in popularity and power, that it has become a great threat to Nigerians. Their fight to instill a government that follows the sharia law in Nigeria is violent and has resulted in many human rights abuses.
- Encroachment of neighboring states that sense government weakness and vulnerability 😧 As mentioned above, the emergence of divisions may cause the government to look weak in the perception of its citizens and other nations. This may result in the government taking extreme measures to maintain its legitimacy, such as annexing another territory.
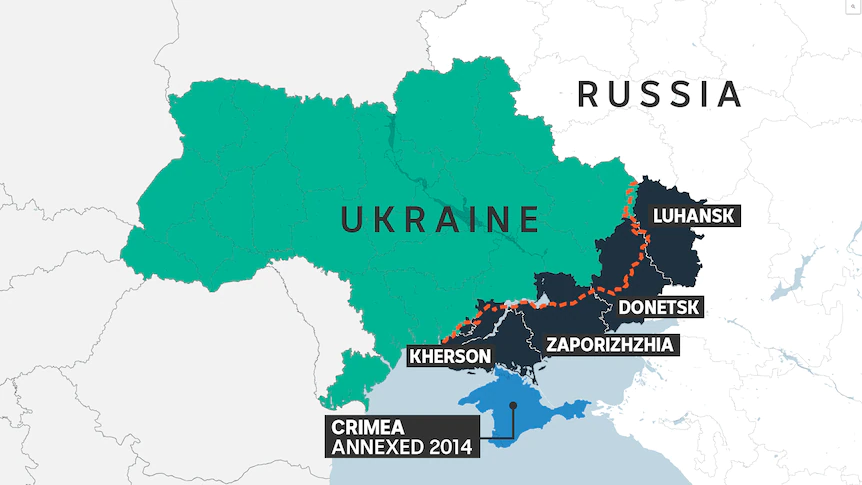
Example: The Russian government's invasion on Ukraine that began in Febraury of 2022 was a shocking attempt of imposing power over state that did not believe in the capacity of the Russian government to resort to violence. As a very extremist strategy, the Russia President Vladimir Putin engaged in a very long and cruel war, to prove Russia's hegemonic power in the region.
Cleavages ➗
As a recap, cleavages are internal divisions typically based on ethnicity, religion, geography, and/or class. Those divisions can become politicized, and this impacts political culture and political behavior. More specifically, the course focuses on how cleavages impact the relationship of citizens with their governments.
State reactions to cleavages can range from brute repression to recognition of ethnic/religious minorities and the creation of autonomous regions and/or representation of minorities in governmental institutions. The way that states react can impact the legitimacy (conformity to the law) citizens give to their regimes. Authoritarian states tend to react much more harshly to social cleavages that become politicized in order to maintain control and order.
Unit 3 - Quick Review! 🤓
This unit is mainly focused on the interactions between the state and society. A country’s political patterns are influenced by the characteristics and demands of its population.
We first explored civil society 🙋♂️which are voluntary associations that are separate from the state but help individuals to interact with the state.
Then, we moved into a discussion of political culture, ideologies, 💭 as well as political beliefs and values. With these topics, we focused on the core beliefs and values that address the tension between order and liberty,🆓 and shape the relationship between a state and its citizens.
The latter half of the unit focuses on how citizens formally and informally participate in politics and the differences in how authoritarian regimes and democratic regimes support or limit participation. In conjunction with participation, we explored how various regimes support or limit individual civil liberties or civil rights. 💪
Finally, we ended the unit with a discussion of how internal divisions, called cleavages, become politicized and impact relationships between groups and the state.
In the next Unit we will talk about Party, Election Systems and Citizen organizations!

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.