<< Hide Menu
Karla Jauregui Sandoval
Karla Jauregui Sandoval
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are a type of non-renewable energy source that are formed from the remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Fossil fuels are the main source of energy for the world's electricity and transportation needs, and they have played a major role in the development of modern society. However, the use of fossil fuels also has negative impacts on the environment, including air pollution and the contribution to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases. As such, there is a growing movement to transition to renewable energy sources and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
The world is dependent on fossil fuels because they are easy to access. The three main types of fossil fuels are coal, oil (petroleum) and natural gas.
- Coal ➱ Formed from millions of years of decomposed plant buildup, coal is made of of carbon, hydrogen and water
- Oil ➱ Formed from millions of years of heat and pressure of aquatic organisms, oil is made up of carbon and hydrogen
- Natural Gas ➱ Formed from plant and animal organic matter trapped under a sedimentary layer of Earth’s layer, natural gas is made up mostly of methane (CH4)
Combustion of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuel combustion is the process of a fuel type reacting with heat and oxygen which leads to chemicals, light and energy being released. Complete combustion releases non-toxic chemicals such as water vapor and heat however in majority of the cases incomplete combustion occurs.
Natural Gas Combustion
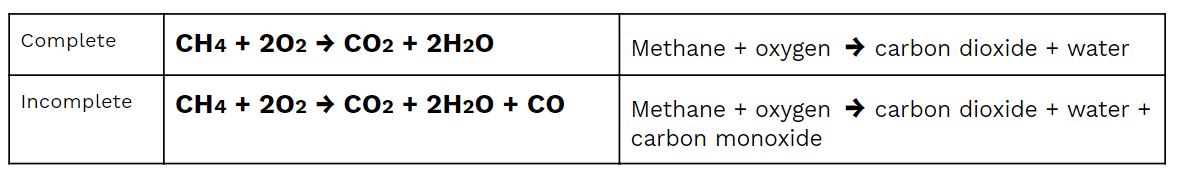
Methane Combustion
Coal Combustion
Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic Fracturing is a process that involves drilling through rock to unlock oil and natural gas in the ground. As mentioned, gas is formed on top of layers of dead organisms that over time have been exposed to pressure.
Hydraulic factoring involves steel cement pipes that pump out fluid. The fluid opens up fractures in the shell, water, sand, and surface. The sand for example allows the oil to go up. As the wheel reaches its kickoff point then that is well the horizontal drilling of the holes allows the oil to escape through the cracks.
Image Courtesy of Mother Earth News
Risks of hydraulic fracking include:
- Contaminating underground drinking water
- Increases threat of earthquakes which puts infrastructure at risk
- Methane is released during drilling
- Natural gas supplies are nonrenewable
- Damaging ecosystems and disturbing local environments with machinery
Impact of Fossil Fuels
An impact of the production and combustion of fossil fuels is the byproduct of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and carbon dioxide.
- When coal is burned, it releases CO2, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, as well as particulates that are known to pollute the atmosphere. As a result of these pollutants being produced, acid rain forms. Acid rain is comprised of any type of precipitation, wet or dry, that combines atmospheric pollutants with water droplets, such as snow and hail. This rain is toxic and harmful to ecosystems around the world.
- The use of oil pollutes the environment through the burning of petroleum, which creates and releases greenhouse gases. Oil is not a clean source of energy as it contributes to global warming due to the release of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide.
- Another impact of oil is the risk of oil spills which are difficult to clean up and can harm marine life at devastating levels.
- Oil is a non-renewable energy source because the pace at which petrol replenishes will not be nearly high enough to satisfy increasing demand. 🎥 Watch: Environmental Science

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.