<< Hide Menu
1.1 Kinematics Overview and Motion in One Dimension
7 min read•june 18, 2024
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Gerardo Rafael Bote
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Gerardo Rafael Bote
Overview
Everybody can see motion! However, motion is more than just moving. Motion is made up of a few different parts. For example, how can you describe the position of your body in relation to time? How can you tell that an object is faster than another? These are some of the questions physicists ask when studying kinematics. This is a MAJOR part of the course as the rest of AP Physics C: Mechanics has some sort of foundation within this unit.
Big Idea
- Change: Interactions produce changes in motion.
- When rolling down a hill, why do you go faster the farther you go?
- If you want to throw a stone as far as you can, why should you throw the stone higher?
Exam Impact
Unit 1 will cover approximately 14%-20% of the exam and should take around 22, 45-minute class periods to cover. The AP Classroom personal progress check has 15 multiple choice questions and 1 free response question for you to practice on.
Kinematics: Motion in One Dimension🚴
To explain motion, you need to know the following terms:
- The position of an object is its location within a certain time frame.
- The displacement of an object is its relative change in position in some reference to some origin. (Δx=x−x0)
- The distance of an object is the length of the path covered by the object.
- The velocity of an object is the rate at which the object's displacement changes over time.
- The speed of an object is the rate at which the object's distance changes over time.
- The acceleration of an object is the rate at which the object's velocity changes over time. ⚠️But, wait... aren't displacement and distance the same thing? Aren't speed and velocity the same thing, too? Well, not exactly. You need to consider that displacement and velocity (and acceleration) are both vector quantities, meaning that they bring both a numerical value (i.e., magnitude) and a direction. Scalar quantities, like distance and speed, only bring a magnitude (no direction included) and are always positive.
For example, in the picture below, the bicyclist's distance traveled would be measured in path A (the road); on the other hand, the bicyclist's displacement from his/her house to the factory would be measured in path B.
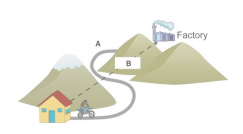
Image from Dan Levine
For vector quantities, a positive number (+) indicates that the object's rate or direction is up or right. A negative number (-) indicates that the object's rate or direction is down or left.
For those who want to visualize displacement, velocity, and acceleration as vector quantities, refer to the graphic below:
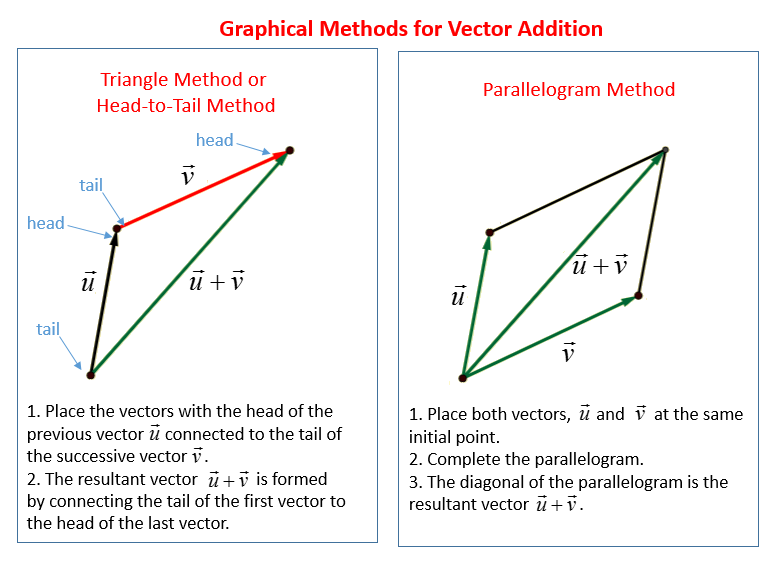
Image from Online Math Learning
Average velocity is a comparison between the displacement and the time required for the displacement to occur. It is approximating motion since the velocity could have increased or decreased during the specified time interval.
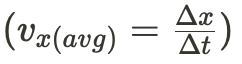
Instantaneous velocity, on the other hand, is the velocity that was measure at a certain time frame. Deriving a position function will allow one to detect an object's velocity at some time frame without using average velocity to estimate it.
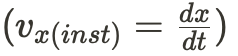
Instantaneous velocity and average velocity are two different measures of velocity that are used to describe the motion of an object.
Here are some key points about instantaneous and average velocity:
- Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a particular instant in time. It is a measure of the speed and direction of the object at a specific moment.
- Average velocity is the total distance traveled by an object over a period of time, divided by the time elapsed. It is a measure of the overall speed of the object over a given time period.
- Instantaneous velocity is a measure of the speed and direction of the object at a specific moment in time, while average velocity is a measure of the overall speed of the object over a given time period.
- Instantaneous velocity is a vector quantity, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction. Average velocity is also a vector quantity, with the direction being the same as the direction of the total displacement of the object over the time period.
There are many ways to represent the relationship between velocity (v), acceleration (a), position (x), and time (t). Know the following equations to understand how they relate
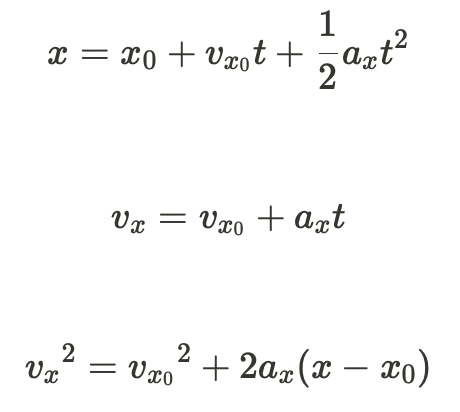
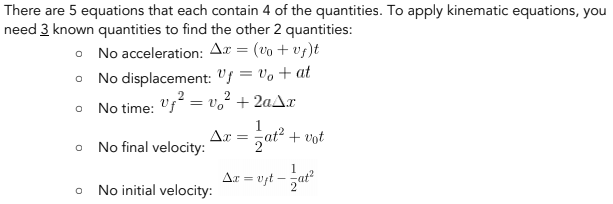
TIP: If you need to solve for a quantity from the above equations, make sure that you can solve it given that you have the other variables filled in! For example, in the 2nd equation, if you have the final velocity, the time interval, and the acceleration rate, then you can solve to figure out the initial velocity!
There is also one more relationship that you should consider:
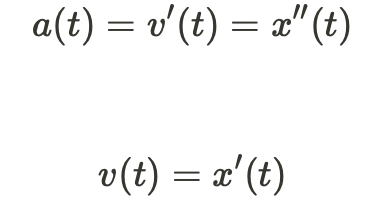
What the equation shows above is that the function representing an object's acceleration is the same function that represents the 1st derivative of the velocity function and the 2nd derivative of the position function. It works the other way too:
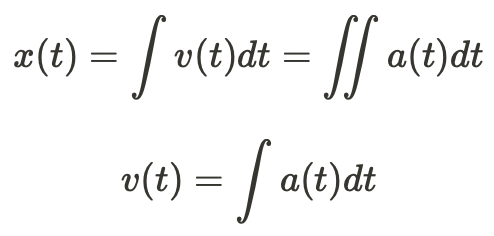
The position function is represented by the integral of the velocity function and the double integral of the acceleration function.
⚠️But, wait... I don't know how to differentiate and integrate... What? You don't know how? There is a reason why this course is called AP Physics C! C means Calculus! Don't worry, here are the basic rules for doing integrals and derivatives for this course:
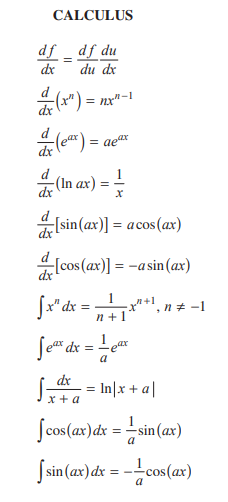
Here are some more tips for using calculus to solve problems in kinematics:
- Review the definitions of displacement, velocity, and acceleration:
-
Displacement is the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity and is typically denoted by the letter "d".
-
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. It is also a vector quantity and is typically denoted by the letter "v".
-
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. It is also a vector quantity and is typically denoted by the letter "a". 2. Understand the concept of a derivative:
-
A derivative is a mathematical operation that calculates the rate of change of a function at a given point. In kinematics, derivatives are used to calculate the velocity and acceleration of an object. 3. Use the formulas for displacement, velocity, and acceleration:
-
Displacement can be calculated using the formula d = d0 + v0t + (1/2)at^2, where d0 is the initial displacement, v0 is the initial velocity, t is the time elapsed, and a is the acceleration.
-
Velocity can be calculated using the formula v = v0 + at, where v0 is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration, and t is the time elapsed.
-
Acceleration can be calculated using the formula a = (v - v0)/t, where v is the final velocity, v0 is the initial velocity, and t is the time elapsed. 4. Pay attention to units:
-
Make sure to use the correct units for your calculations. For example, displacement is typically measured in meters (m), velocity is typically measured in meters per second (m/s), and acceleration is typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2). 5. Consider the reference frame:
-
When solving problems involving kinematics, it is important to consider the reference frame from which the motion is being observed. This can affect the values of the variables in your calculations. 6. Use graphs to visualize the motion:
-
Graphs can be a useful tool for visualizing and understanding the motion of an object. For example, a graph of displacement vs. time can show the position of an object at different times, and a graph of velocity vs. time can show how the object's speed is changing. 7. Practice, practice, practice:
-
The best way to improve your skills in using calculus to solve problems in kinematics is to practice solving a variety of problems. This will help you become more familiar with the concepts and techniques involved and improve your problem-solving skills.
If you're given a kinematic graph (i.e., a graph containing time and some other measure), use the following table to figure out what part of the graph you need to solve for:
Kinematic Graphs
| Types of Kinematic Graphs | Area Under Curve | Slope | Magnitude of Y-value |
| Position vs. Time | N/A | Velocity | Distance from detector or starting position |
| Velocity vs. Time | Change in Position | Acceleration | Speed of Object |
| Acceleration vs. Time | Change in Velocity | Jerk* (Not Tested in AP Exam) | Acceleration |
Use the following table to describe the vector quantities:
Vector Quantities
| Vector | Negative (-) | Zero (0) | Positive (+) |
| Displacement | You are now south, west, left, or in the -x or -y direction of your starting position. | You are back at your starting position. | You are now north, east, right, or in the +x or +y direction of your starting position. |
| Velocity | You are traveling south, west, left, or in the -x or -y direction. | You are at rest. | You are traveling north, east, right, or in the +x or +y direction. |
| Acceleration | If your velocity > 0, your speed is decreasing in a positive direction. If your velocity < 0, your speed is increasing in a negative direction. | You are at rest OR you are moving at a constant velocity. | If your velocity > 0, your speed is increasing in a positive direction. If your velocity < 0, your speed is decreasing in a negative direction. |
Practice Question:
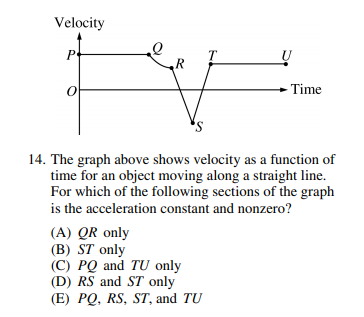
Image from collegeboard.org
Answer
The correct answer is D. To show a constant acceleration on a velocity vs. time graph, you need to consider the slope of each line segment. For constant acceleration, it is shown through a straight slope (not curved) on a velocity vs. time graph; therefore, QR cannot be it. For acceleration to be nonzero as well, the slope of the velocity vs. time graph cannot be horizontal, marking out PQ and TU. Therefore, RS & ST satisfy the question.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.