<< Hide Menu
Isabela Padilha
Isabela Padilha
In the previous guide, Topic 1.3 - Contemporary Life, we looked at the challenges that hispanohablante families face. In this guide, we will delve deeper into the Global Challenges that relate to spanish speaking populations to give you a better insight of the geopolitical, social, environmental and economic state of these nations.
Essential Questions/Preguntas Esenciales
- What environmental, political, and social issues pose challenges to societies throughout the world/¿Cuales retos ambientales, políticos y sociales plantean retos a la sociedad a lo largo del mundo?
- What are the causes of those issues?/ ¿Que causan estes problemas?
- What are possible solutions to these challenges?/¿Cuales son las posibles soluciones a estes retos?
Economic Issues
Latin American countries and Spain have adopted economic systems that were shaped by its historical developments. As a developing nation, Latin America still struggles a lot economically, as a consequence of political instability, corruption, and poor governmental management. In the table below, you can observe the levels of poverty and income distribution in the region:
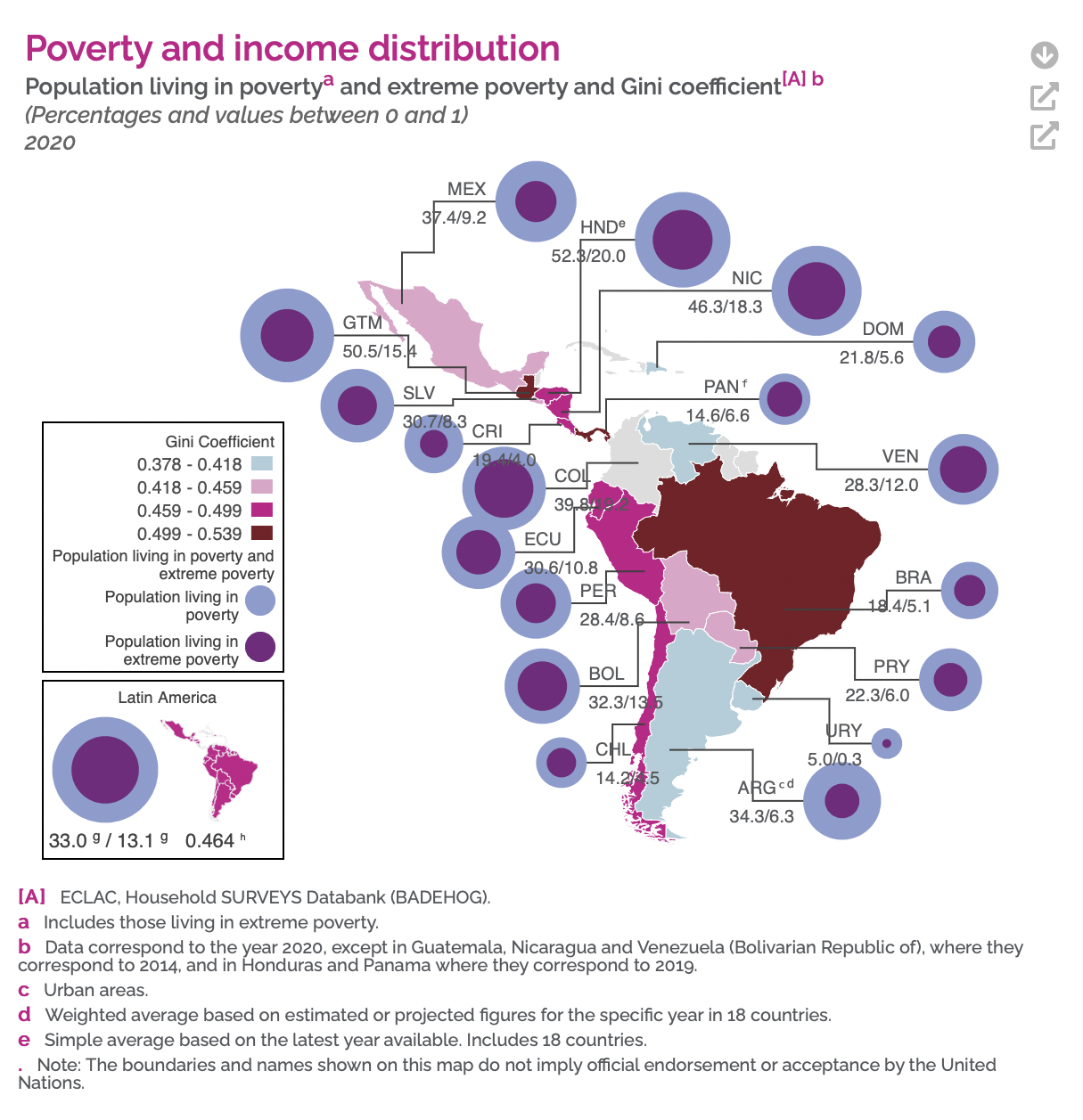
Here are a few issues experiences by the region:
- Income inequality - Latin America is known for being one of the most unequal regions in the world. Although different nations have adopted different economic policies, most of them have one aspect in common: strong elites. Elites that have influence in the government are able to shape policies to increase their wealth while sustaining poverty in the lower classes.
- Weak Institutions - As many Latin American nations are young democracies, their lack of guidance results in the weakening of political institutions. This results in slower economic growth.
- Lack of Infrastructure - The lack of infrastructure in Latin America has many causes, and corruption is one of the principal ones. It slows economic growth and reduces quality of life.
Key words: Desigualdad, instituciones débiles, infraestructura, desarollo económico.
Religious - El papel de la religión
Religion has played a major role in the poltiical development of the region. The majority of the population identifies as Christian, with Catholicism being one of the most followed one.
What are the political impacts of religion in países hispanohablantes?
When Spanish Catholics arrived in the region during the colonization period, their goal was to convert and spread Catholicism. Still today, christian values are emphasized in several areas of latinx people's lives, such as in education, healthcare, and social services.
Recent challenges to the supremacy of the Catholic Church, through the rise of Evangelical Protestantism in the region, have resultes in conflict. Political actors across the region compete with each other on the basis of religion.
Key words: religión, catolicismo, cristianismo, sistema de salud, colonización.
Ideological conflicts
Even though Latin America has been widely shaped by the western style of government, a few countries have experiences ideological revolutions that challenge that western structure. One of these countries is Cuba 🇨🇺
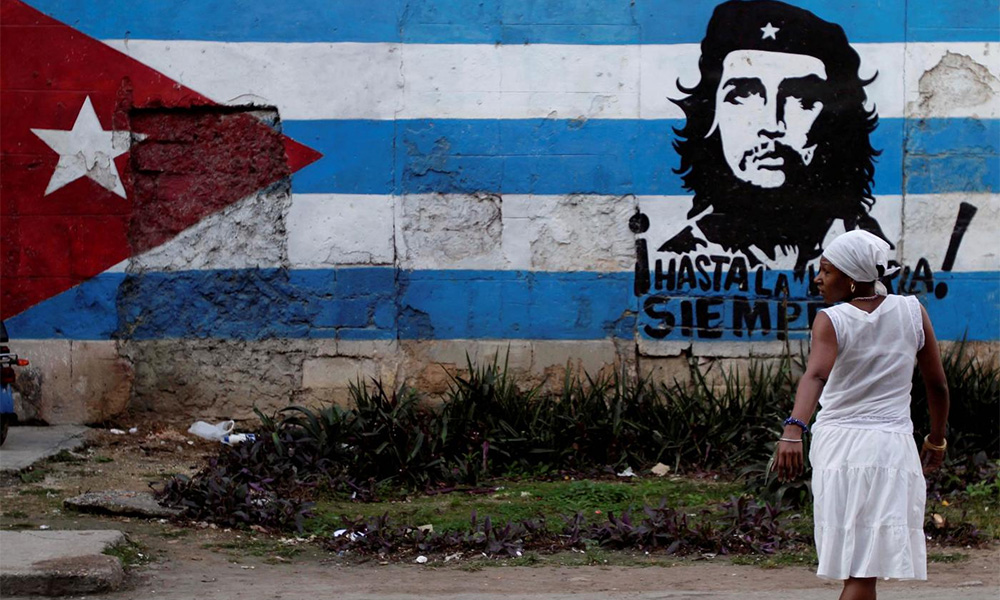

The Cuban Revolution of 1959 was led by Fidel Castro, and it established socialism in the country. Since then, the government has focused on implementing policies to reduce poverty, inequality, and improving access to healthcare and education.
After the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, Cuba lost its main trade and economic aid partner, leading to many issues to its economic system. The country still faces a lot of economic and political challenges, but many policies have been adopted over the last few decades to mitigate these negative impacts.
Key words: Revolución, socialismo, retos económicos y políticos, ideologia.
Pandemic Impact:
It is also important to recognize that a lot of these issues have either shifted or have been aggravated by the Covid-19 pandemic. Spanish-speaking countries, especially in Latin America, are still dealing with the social and economic consequences of this phenomenon and there has been an increase in poverty, inequality and famine across the regions.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.